3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
Several decades ago, thermal imaging sensors were primarily deployed in the government and defense sector. FLIR has been the industry leader in developing new thermal solutions designed for broader markets such as security. Today, FLIR thermal cameras have the standard for 24-hour monitoring for critical infrastructure perimeter security and beyond.
The value proposition for thermal cameras is simple. They capture clear images in harsh environments where conventional cameras simply can’t perform. While traditional visible light cameras struggle to produce quality images in adverse conditions, such as rain, fog or complete darkness—thermal cameras enable 24-hour monitoring and deliver high-contrast images, ideal for video analytics and accurate intrusion detection. This ability proves itself invaluable when it comes to threat recognition, real-time response and crime prevention for mission-critical sites.
The mechanics behind thermal technology is simple. All objects emit heat, including plants, animals, people, cars, etc. Because thermal sensors create images based on the detection of minute differences among heat signatures of different objects, they can deliver clear images in low-light or no-light scenarios.
Thermal technology has proven its reliability time and time again, enhancing human detection, reducing false alarms and improving perimeter protection at airports, electrical substations, nuclear power plants, data centers and other critical infrastructure locations.
When considering integrating thermal cameras into your perimeter intrusion detection system, keep in mind that not all thermal cameras are equal. Consider these three features that set apart superior thermal cameras from standard options:
1. RESOLUTION AND DETECTION RANGES
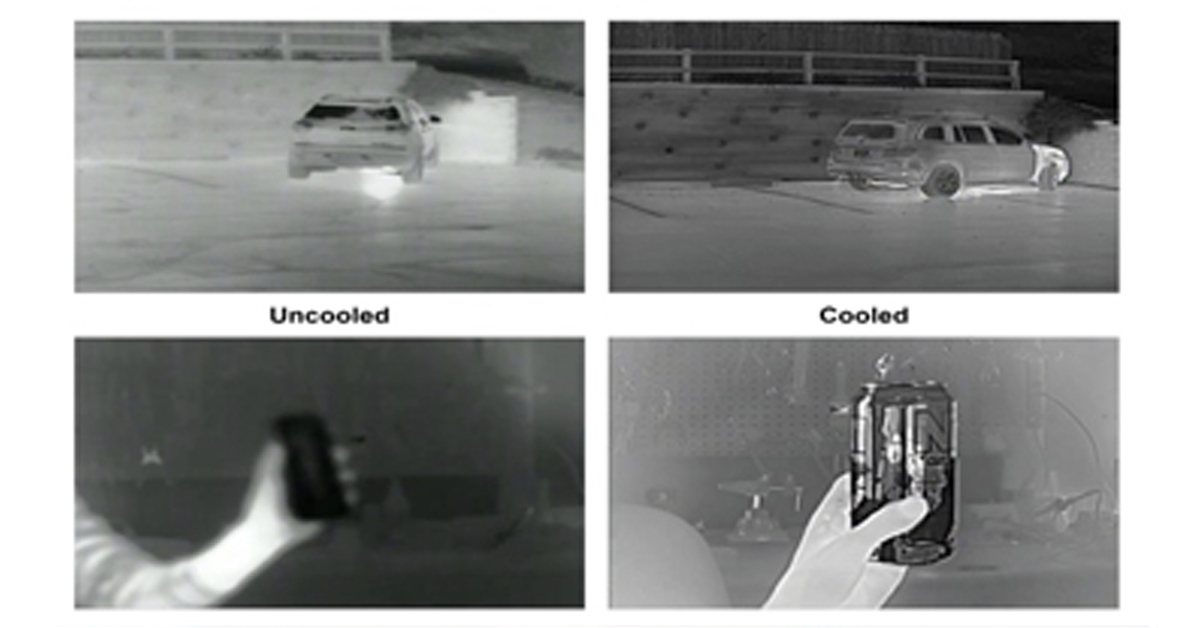
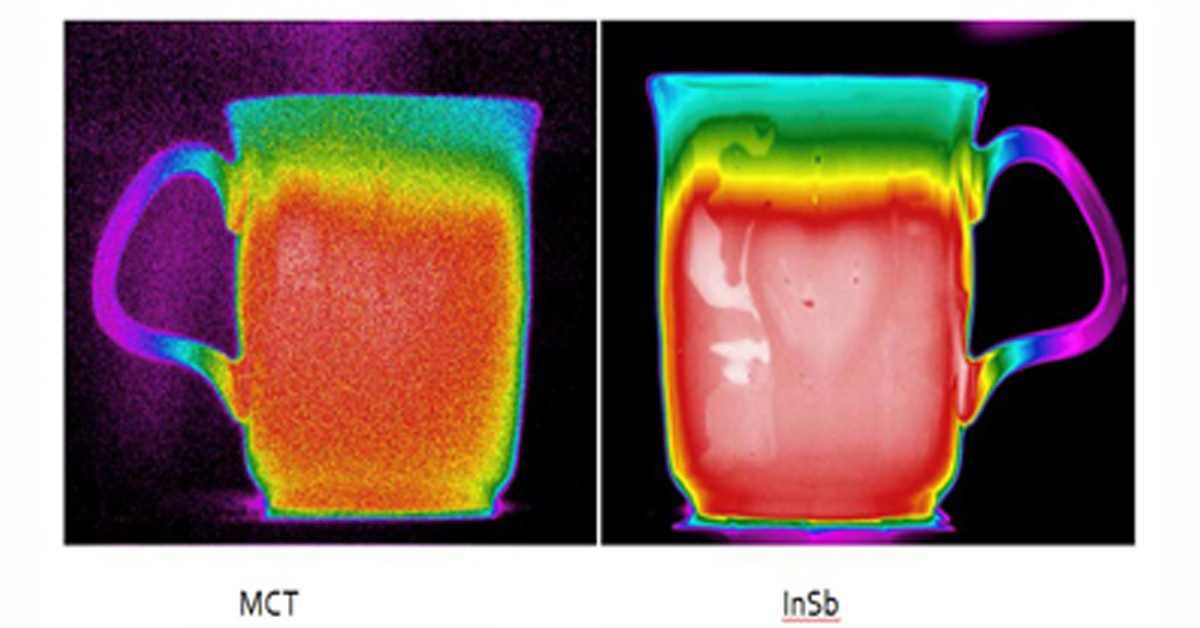
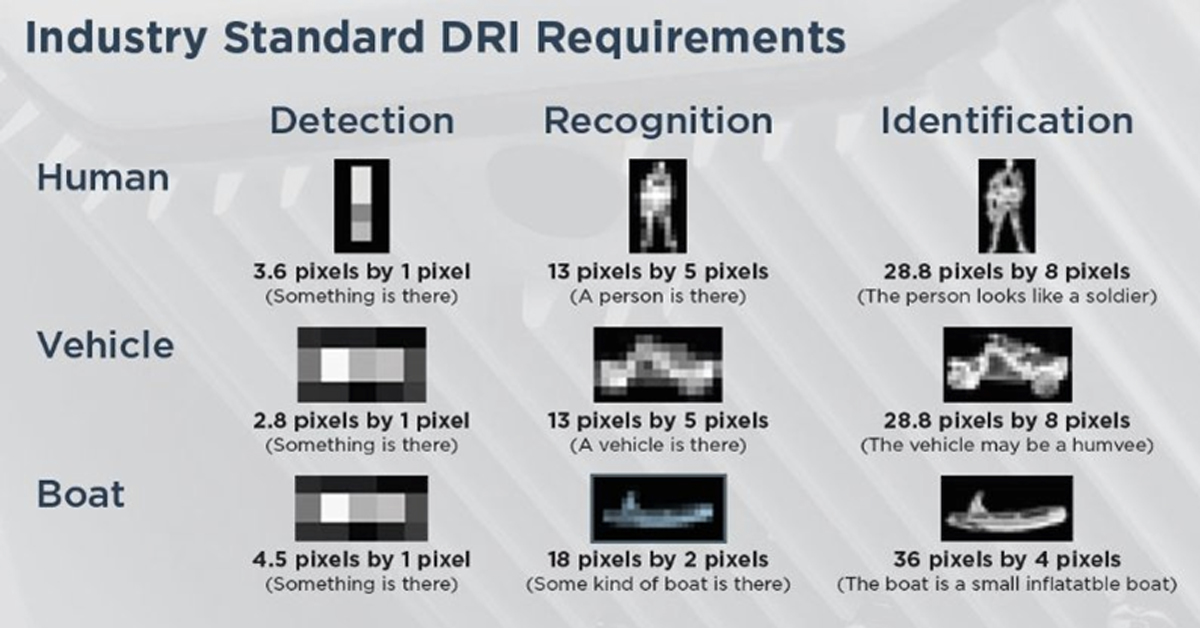
High-quality thermal cameras are known for their superior resolution options and longer detection ranges. When choosing a thermal camera, it is vital that you select a resolution appropriate for each application. For critical infrastructure deployments, where cameras need to detect objects well beyond the fence line, sensors with full thermal resolution of 640×480 are a must. These devices can offer up to 16 times as many pixels as the standard thermal camera, allowing much longer detection ranges and delivering greater image detail, both of which are crucial to analytic performance at these extended ranges. When it comes to commercial installations that need wide-area monitoring and a detection range of 50 meters, 320×120 resolution is optimal.
2. BUILT-IN ANALYTICS
Thermal cameras that can both disseminate and classify alerts greatly enhance the capability of security installations. It is one thing to detect an object; it is another thing to be able to define what that object is. As artificial intelligence continues to drive product development across the security industry, superior thermal cameras reliably differentiate between types of objects, such as humans and vehicles, in order to relay more detailed information. Backed with image enhancing features, exceptional thermal cameras produce sharper, crisp images that enable accurate, actionable alerts, reduce false alarms and lower the overall cost of ownership of the solution.
3. INTEROPERABILITY
For every security solution, it is important to ensure devices at the edge are compatible with video management systems. Integrators should look for thermal cameras that are ONVIF-compliant and that stream digital video in H.264, in order to guarantee interoperability and adoption by third-party providers.
These features set first-class thermal cameras apart from low-end thermal camera options. When it comes to selecting a thermal camera, make sure you and your customer know which technology features will ensure optimal performance.
Blog Posts

Thermal Camera Selection
How Far Can I See?

How Should Human Temperature Be Measured?

What is Wide Dynamic Range?

MYNOISE AUDIO MIXER REVIEW

WHAT IS A WIRELESS DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?

POE VS. POE+ VS. POE++: CHOOSING THE RIGHT INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCH FOR YOU

INDUSTRY-LEADING INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCHES
UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER

5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET AND REGULAR ETHERNET

INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING EQUIPMENT USED FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES

CYBERSECURITY: PROTECTING INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS

HOW INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING CAN PROVIDE SECURITY FROM DRONES
.webp)
Thermal Cameras Reveal How to Keep Your Home Cool During a Heat Wave

FLıR ONE PRO
.png)
Unmatched Maritime Awareness with Cooled Thermal Imaging
.png)
What Is the Right Handheld Thermal Camera for You?
.png)
Camera Resolution and Range
.png)
Special Applications for Marine Cameras
.png)
What’s The Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
.png)
Can Thermal Imaging See Through Fog and Rain?

Which Cx-Series Camera Is Right for You?
.png)
What is MSX®?

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging
.png)
3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
.png)
Determine Which Visible and Thermal Security Cameras You Need

Bullet vs. PTZ vs. Dome: Which Security Camera Is Right for You?

Interfaces for Machine Vision

Machine Vision Sensor Review
.png)
Teledyne FLIR, the Industry Leader, Launches Boson +, a Long-Wave Infrared Thermal Imager Module with an Accuracy of Less Than 20 mK
.png)
Whitepaper: IP-Based Security Convergence
.png)
3 Technologies Transforming Safe Cities into Smart Cities
.png)
Insights from the Field: Ensuring Workplace Safety Using Thermal Camera Screening for Entry Control

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier

Can Thermal Imaging See Through Walls? And Other Common Questions
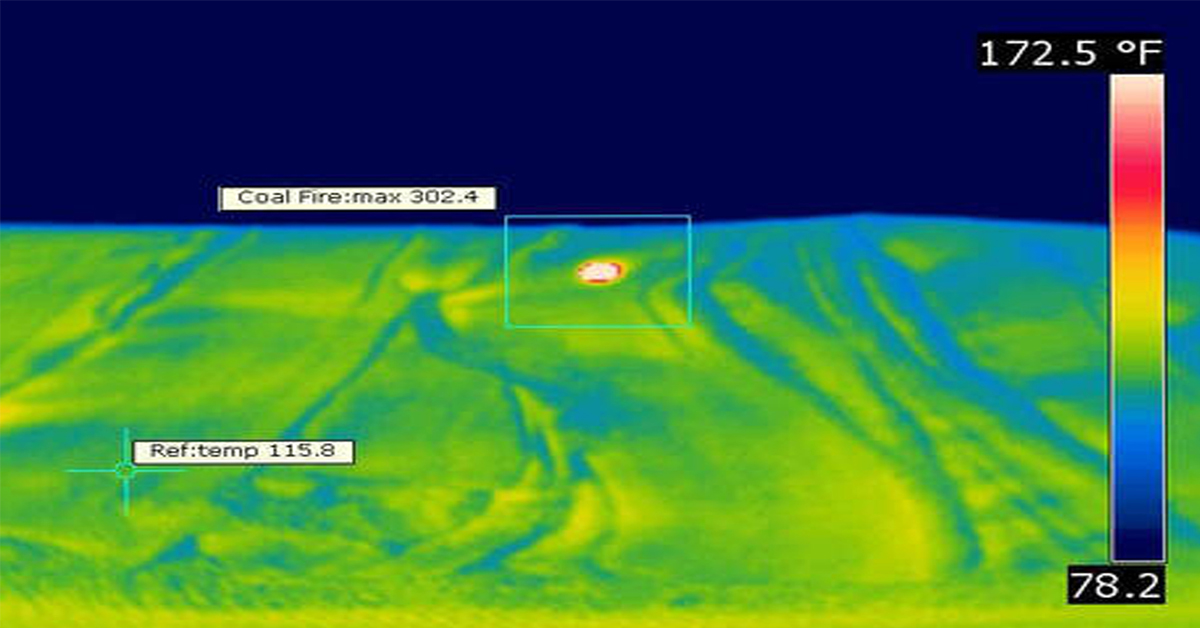
Application Spotlight: Early Fire Detection for Rapid Heat Generation

Protect Personnel and Equipment by Detecting Early Signs of Fire

Teledyne FLIR Launches A500f/A700f Cameras for Fire Detection and Condition Monitoring

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help Guarantee Fire Safety in Tunnels

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help to Prevent Fires

ITS-Series Dual AID Surpasses Standards for Fire Detection Systems in Japan

How Layering Multispectral PTZ Cameras and Radars Improve Perimeter Protection
POWER REMOTE RESET TECHNOLOGY - PRRT

Why Yacht Owners are Adding Thermal Imaging Cameras to Minimise the Risk of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires?
.png)
Intelligent Transportation Systems

Best Practices Guide for Perimeter Security Applications

Protect Pedestrians, Bicyclists and More with Thermal Smart Sensors

White Paper: Application of Ground-Based Security Radar to Perimeter Systems

What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks

Battery Inspection Using Advanced Thermography

Providing ire Protection for Lithium Battery Storage

The Power of Thermal Imaging
.png)
Why Panel PCs Are Perfect For Industrial Applications?

Teledyne DALSA
.png)
Advantages of Virtual Barrier Video Analytics for Perimeter Security Systems
.png)
.png)
NASA Takes the Teledyne FLIR Boson Thermal Camera Module Out of this World
.png)
Port Security Enhancement: DP World Yarımca's Trust in FLIR Security Solutions for Effective and Safe Port Operations
.png)
The Importance of Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) for Detection Accuracy
.png)
Bosphorus Boat Show 2025: The Meeting Point of the Maritime World

Application Spotlight: Critical Asset Monitoring for Thermal Conditions
.png)
Thermal Imaging for Marine Firefighting
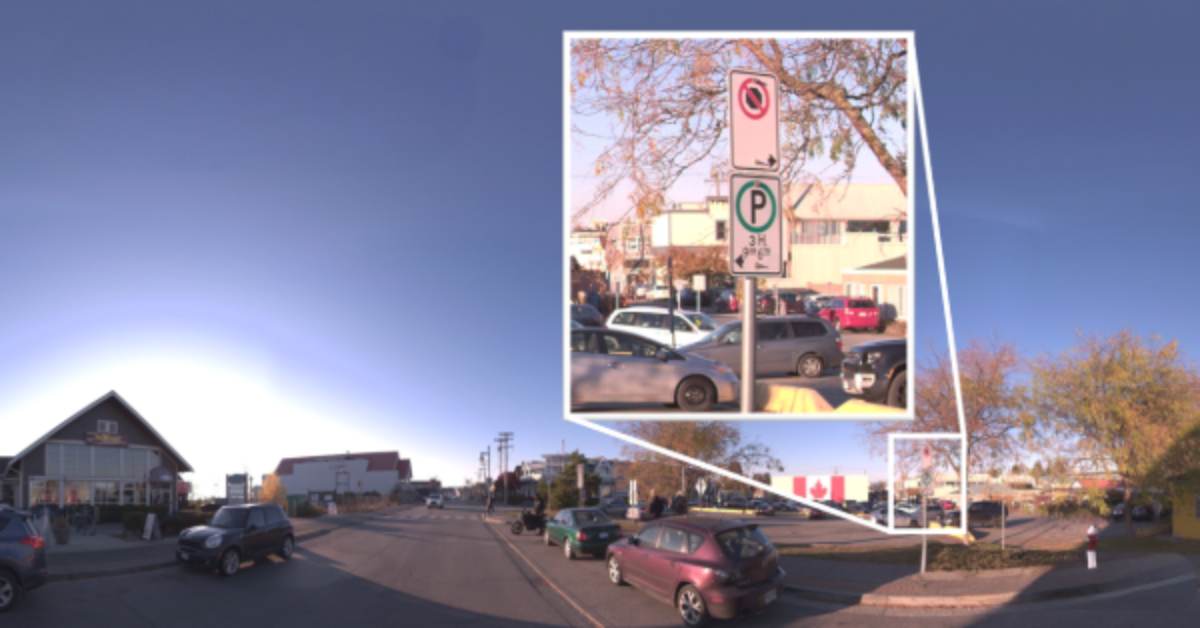

Imaging in Mobile Mapping
.png)
Using Thermal Imaging for Oil Spill Detection

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging

Case Study: Tackling Compressed Air Leaks in Automotive Parts Manufacturing with Acoustic Imaging

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
.png)
Line Scan Contact Image Sensor - AxCIS

Beyond Resolution: What Really Makes a Camera System Work for Mobile Mapping
.png)
Multispectral Marine Cameras for USV Applications
.png)
Stabilizing FLIR Cameras for Smooth Viewing in Rough Waters
 (1).png)