How Far Can I See?
Target Detection
The resolution required for the detection of an object is determined by the obtained pixels. The Johnson Criteria, which are used worldwide, apply here. These criteria were established in the 1950s.
Criterion:
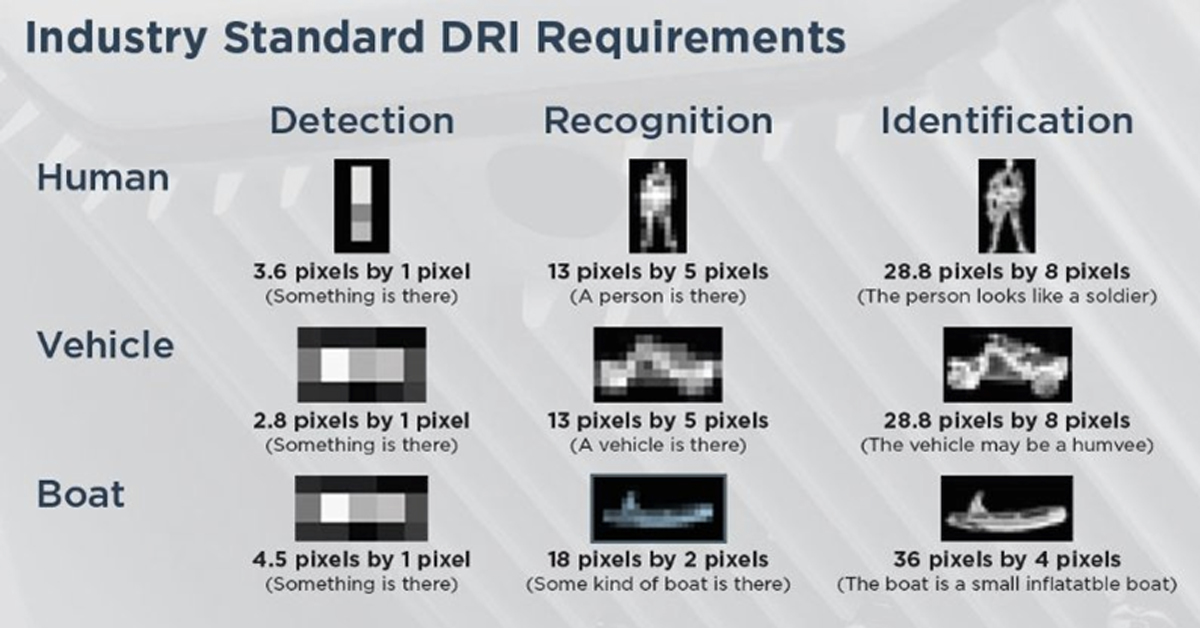
The 50% probability detects the pixels that objects of various sizes will occupy for a temperature difference of 20C. The criterion consists of 3 main parts. These;
- Detection: Indicates that an object exists.
- Recognition: Indicates what an object is. (like truck, human)
- Identification: Indicates how an object is. (Man with gun, like F16)


Factors in Target Detection
- Detector Resolution
- Field of View (Field of View)
- Optical Zoom
- Heat Sensitivity
- Fog, Rain and Snow

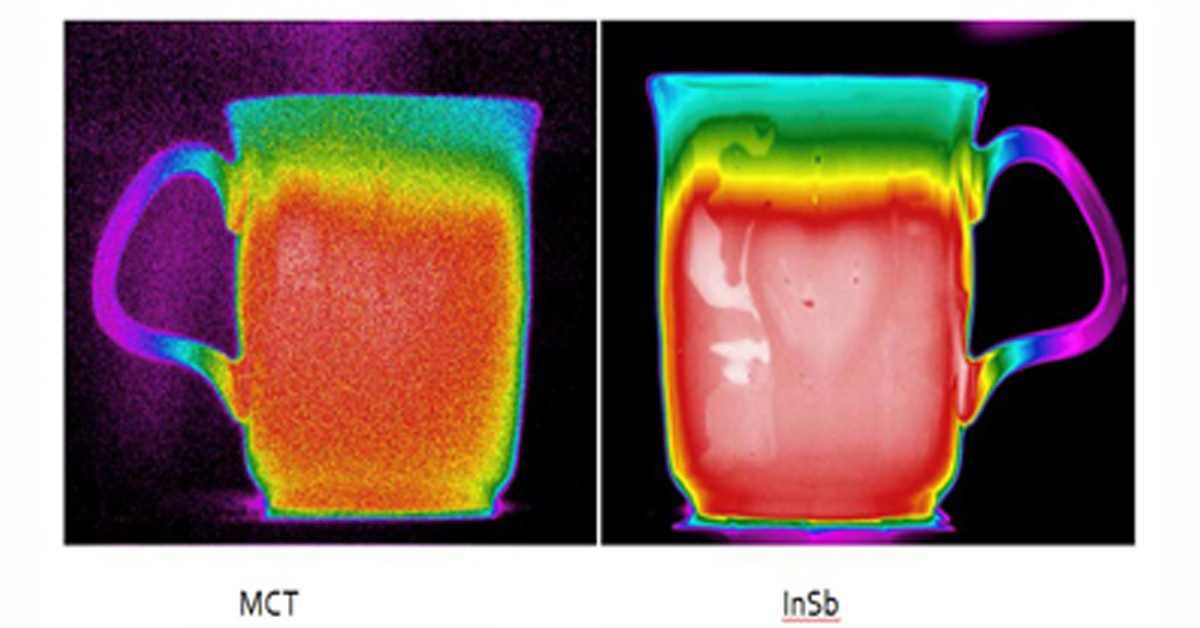
As the detector resolution increases, the target data increases, making identification easier.
Field of View (FoV)

As the angle of view increases, it is necessary to decrease the distance in order to see the same image. Therefore, smaller viewing angles allow for more remote detection.


With the same optical lens (2000 mm), the pixels occupied by the object at different distances in the detector are reduced. Therefore, diagnosis becomes difficult. In order to improve this, the optical lens should be enlarged further, that is, the angle of view should be narrowed.
OPTICAL ZOOMING

Optical zooming is actually changing the angle of view by changing the distance between the lens used and the detector. In this way, the amount of data falling on the detector changes without any manipulation on the original image. In this way, target identification becomes easier. While wide area scanning can be performed thanks to optical zoom, a detected target becomes detectable by optical zoom.
DIGITAL ZOOMING

When digital zooming is applied over optical zoom, the image is enlarged by a factor of two.
Target and Range

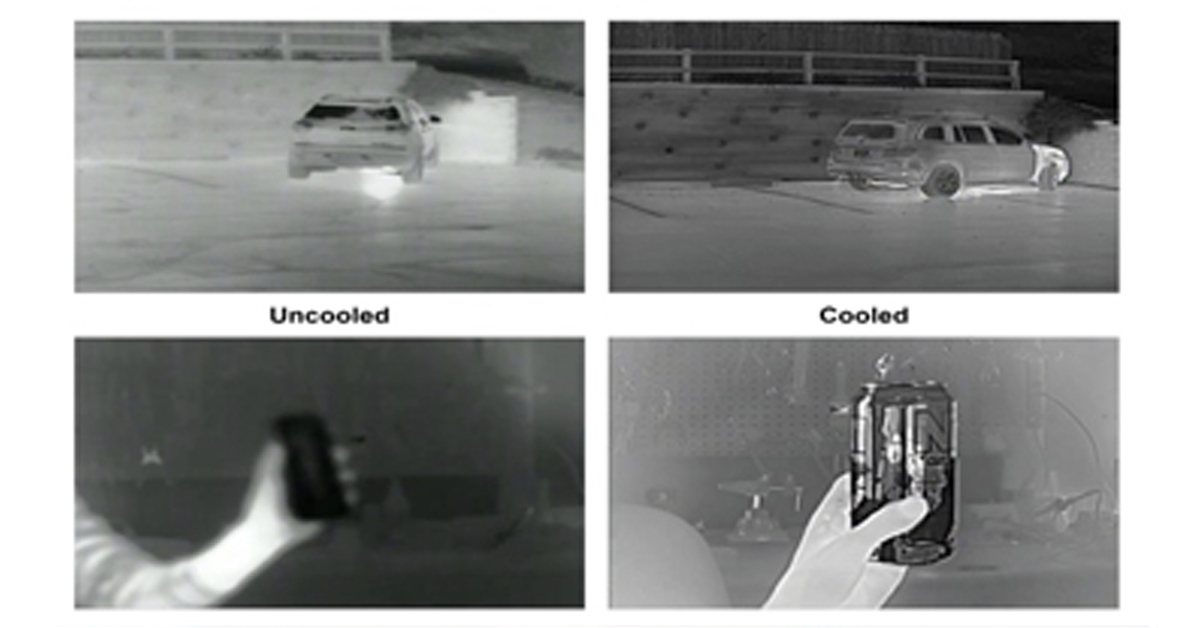
Heat Sensitivity

As the distance increases, the temperature differences between the objects decrease due to meteorological conditions. Therefore, there is a need to detect small temperature changes over long distances. Cameras with high heat sensitivity can detect these differences and create more sensitive and clear images.
Fog

Normal Camera Thermal Camera
The heat is absorbed by the water molecules in the air and therefore the temperature value decreases over long distances. In cases such as fog, the water molecules in the air are less against situations such as rain, so heat permeability is high. In this way, thermal cameras can provide images.
Snow

Due to low temperature differences in snowy weather, it is difficult to detect the environment in particular. However, the detection of objects can be achieved thanks to the temperature differences between the objects and the background. Although it is a factor in range, it does not prevent target detection.
COMPARISON

In the examples above, the effect of the number of detector pixels on the detection distance can be seen. The number of pixels covered by a 2.3 x 2.3 m target at 300 m distance, with all conditions the same, was calculated at different detector resolutions.

In the examples above, the effect of the field of view (FOV) on the detection distance can be seen. The number of pixels covered in different fields of view by a 2.3 x 2.3 m target at 300 m distance, with all conditions the same, was calculated.
Blog Posts

Thermal Camera Selection
How Far Can I See?

How Should Human Temperature Be Measured?

What is Wide Dynamic Range?

MYNOISE AUDIO MIXER REVIEW

WHAT IS A WIRELESS DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?

POE VS. POE+ VS. POE++: CHOOSING THE RIGHT INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCH FOR YOU

INDUSTRY-LEADING INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCHES
UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER

5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET AND REGULAR ETHERNET

INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING EQUIPMENT USED FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES

CYBERSECURITY: PROTECTING INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS

HOW INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING CAN PROVIDE SECURITY FROM DRONES
.webp)
Thermal Cameras Reveal How to Keep Your Home Cool During a Heat Wave

FLıR ONE PRO
.png)
Unmatched Maritime Awareness with Cooled Thermal Imaging
.png)
What Is the Right Handheld Thermal Camera for You?
.png)
Camera Resolution and Range
.png)
Special Applications for Marine Cameras
.png)
What’s The Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
.png)
Can Thermal Imaging See Through Fog and Rain?

Which Cx-Series Camera Is Right for You?
.png)
What is MSX®?

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging
.png)
3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
.png)
Determine Which Visible and Thermal Security Cameras You Need

Bullet vs. PTZ vs. Dome: Which Security Camera Is Right for You?

Interfaces for Machine Vision

Machine Vision Sensor Review
.png)
Teledyne FLIR, the Industry Leader, Launches Boson +, a Long-Wave Infrared Thermal Imager Module with an Accuracy of Less Than 20 mK
.png)
Whitepaper: IP-Based Security Convergence
.png)
3 Technologies Transforming Safe Cities into Smart Cities
.png)
Insights from the Field: Ensuring Workplace Safety Using Thermal Camera Screening for Entry Control

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier

Can Thermal Imaging See Through Walls? And Other Common Questions
Application Spotlight: Early Fire Detection for Rapid Heat Generation

Protect Personnel and Equipment by Detecting Early Signs of Fire

Teledyne FLIR Launches A500f/A700f Cameras for Fire Detection and Condition Monitoring

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help Guarantee Fire Safety in Tunnels

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help to Prevent Fires

ITS-Series Dual AID Surpasses Standards for Fire Detection Systems in Japan

How Layering Multispectral PTZ Cameras and Radars Improve Perimeter Protection
POWER REMOTE RESET TECHNOLOGY - PRRT

Why Yacht Owners are Adding Thermal Imaging Cameras to Minimise the Risk of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires?
.png)
Intelligent Transportation Systems

Best Practices Guide for Perimeter Security Applications

Protect Pedestrians, Bicyclists and More with Thermal Smart Sensors

White Paper: Application of Ground-Based Security Radar to Perimeter Systems

What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks

Battery Inspection Using Advanced Thermography

Providing ire Protection for Lithium Battery Storage

The Power of Thermal Imaging
.png)
Why Panel PCs Are Perfect For Industrial Applications?

Teledyne DALSA
.png)
Advantages of Virtual Barrier Video Analytics for Perimeter Security Systems
.png)
.png)
NASA Takes the Teledyne FLIR Boson Thermal Camera Module Out of this World
.png)
Port Security Enhancement: DP World Yarımca's Trust in FLIR Security Solutions for Effective and Safe Port Operations
.png)
The Importance of Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) for Detection Accuracy
.png)
Bosphorus Boat Show 2025: The Meeting Point of the Maritime World

Application Spotlight: Critical Asset Monitoring for Thermal Conditions
.png)
Thermal Imaging for Marine Firefighting

Imaging in Mobile Mapping
.png)
Using Thermal Imaging for Oil Spill Detection

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging

Case Study: Tackling Compressed Air Leaks in Automotive Parts Manufacturing with Acoustic Imaging

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
.png)
Line Scan Contact Image Sensor - AxCIS

Beyond Resolution: What Really Makes a Camera System Work for Mobile Mapping
.png)
Multispectral Marine Cameras for USV Applications
.png)
Stabilizing FLIR Cameras for Smooth Viewing in Rough Waters
 (1).png)